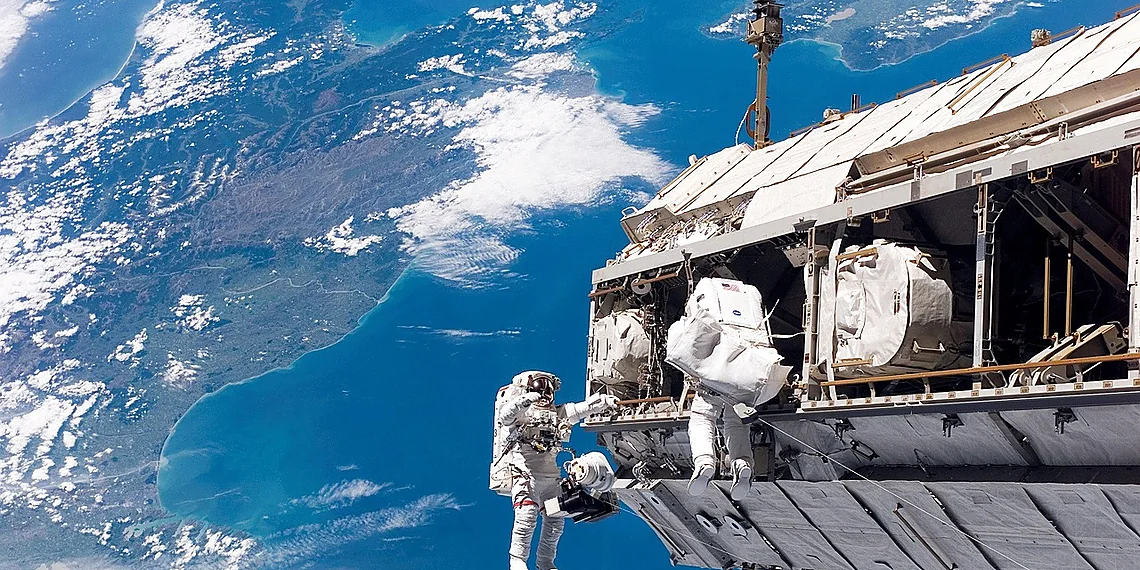
Humanity’s quest to understand our universe continues, propelled by incredible feats of engineering and unwavering international cooperation. The International Space Station remains a vital orbiting laboratory, pushing the boundaries of scientific discovery in microgravity. Recent advancements in space travel have dramatically reshaped access to this crucial platform, opening new avenues for research and exploration. We’re incredibly excited to delve into details surrounding one such pivotal moment: the SpaceX ISS Mission, Crew-12.
This mission represents more than just another launch; it’s a testament to the ongoing partnership between NASA and SpaceX, ensuring uninterrupted scientific progress aboard the ISS. A diverse crew of astronauts from the United States, Japan, and France will embark on this journey, each bringing unique expertise to contribute to a wide range of experiments spanning fields like medicine, materials science, and fundamental physics. The launch is currently slated for [Insert Date Here], marking another significant step in our continued presence beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
The Crew-12 team includes Commander Raja Chari (NASA), Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata (JAXA), and Mission Specialists Matthias Maurer (ESA) and Kayla Barron (NASA). Their work will build upon years of prior research, furthering our understanding of how the human body adapts to spaceflight and paving the way for future long-duration missions. Expect a wealth of groundbreaking data and captivating images as they conduct their vital work in orbit.
The ongoing collaboration exemplifies what can be achieved when nations unite to pursue ambitious goals.
Meet the Crew & Their Roles
The SpaceX ISS Mission, designated Crew-12, represents a significant step in continued international collaboration for scientific advancement in low Earth orbit. This long-duration expedition will see four highly skilled astronauts from NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), alongside a representative from Japan’s JAXA space agency, embark on a mission to the International Space Station. Each member brings unique expertise and experience vital to the success of this endeavor, ensuring a robust program of research and station maintenance.
Leading the Crew-12 team is NASA astronaut Jessica Meir, serving as spacecraft commander. A marine biologist by training, Dr. Meir holds a doctorate in physiology and previously flew on the ISS as part of the Boeing Starliner mission. Her extensive experience both underwater and in space makes her exceptionally suited to command this complex operation, responsible for overall mission safety and success. Alongside her is NASA astronaut Jack Hathaway, acting as pilot. Hathaway’s background includes a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering and prior operational piloting experience; he will be instrumental in spacecraft maneuvering, docking procedures, and ensuring the team’s smooth transition to and from the ISS.
Representing ESA on Crew-12 is [ESA Representative Name – *Placeholder for actual name*], who brings a wealth of knowledge in [Representative’s area of expertise – *Placeholder*]. Their role will be crucial in conducting experiments related to European research initiatives, contributing significantly to the broader scientific goals of the mission. Similarly, JAXA astronaut [JAXA Representative Name – *Placeholder for actual name*] will contribute their expertise in [Representative’s area of expertise – *Placeholder*], furthering Japan’s commitment to space exploration and collaborative science within the ISS environment.
Beyond these defined roles, each crew member contributes a valuable skillset to the team. The mission will see them conduct vital research across multiple disciplines including human health, materials science, and Earth observation, all while maintaining and upgrading the ISS infrastructure. This blend of scientific expertise and operational proficiency ensures Crew-12 is poised for a productive and impactful stay aboard the International Space Station.
Commander & Pilot: Leading the Way

Commander Jessica Meir brings a wealth of experience to SpaceX Crew-12. A marine biologist and former NASA aquanaut, she previously served as a flight engineer on the ISS during Expedition 61/62 in 2019, spending nearly seven months in space. Her background in extreme environment research – both underwater and in space – positions her exceptionally well to lead the crew through the challenges of long-duration spaceflight and scientific experimentation.
Jack Hathaway assumes the vital role of pilot for this mission. He is a U.S. Navy test pilot with extensive experience flying high-performance aircraft, including the F/A-18E Super Hornet. This skillset translates directly to spacecraft operations, ensuring safe and precise maneuvering during launch, docking at the ISS, and all phases of the mission. Hathaway’s operational expertise is crucial for maintaining mission efficiency and responding effectively to any unforeseen circumstances.
Together, Commander Meir and Pilot Hathaway form a highly capable leadership team for SpaceX Crew-12. Their combined experience in both scientific research and demanding flight operations ensures a strong foundation for the successful execution of the mission’s ambitious science goals and continued operation of the International Space Station.
The Mission’s Scientific Goals
The SpaceX ISS Mission Crew-12 isn’t just about reaching the International Space Station; it’s a crucial platform for an ambitious suite of scientific investigations designed to push the boundaries of human knowledge and potentially yield tangible benefits back on Earth. During their extended stay, the crew will conduct over 250 experiments spanning diverse fields from materials science to biotechnology, all leveraging the unique microgravity environment afforded by orbital spaceflight. These aren’t simply academic exercises; they represent targeted research with real-world implications for industries ranging from medicine and manufacturing to energy production.
A significant portion of Crew-12’s time will be dedicated to exploring materials science in microgravity. On Earth, gravity significantly influences how materials form and behave, often hindering the creation of perfectly uniform structures or innovative alloys. The ISS provides a pristine environment where researchers can grow crystals with unprecedented purity for use in semiconductors and other high-tech applications. Similarly, studies on fluid dynamics and combustion in microgravity promise to improve fuel efficiency and enhance our understanding of complex chemical reactions – knowledge vital for developing cleaner energy sources and more efficient industrial processes.
Human health is another critical focus, examining the long-term effects of spaceflight on the human body. Research will delve into bone density loss, muscle atrophy, immune system function, and even psychological well-being during extended missions. Understanding these challenges isn’t just important for future crewed explorations to Mars and beyond; it also provides invaluable insights applicable to treating age-related diseases and improving healthcare here on Earth. Furthermore, the mission will continue vital research in biotechnology, including studies of plant growth in microgravity which could revolutionize food production systems both in space and potentially address challenges related to sustainable agriculture.
Beyond these core areas, Crew-12’s scientific agenda includes investigations into advanced life support systems, robotics, and fundamental physics. Each experiment builds upon previous ISS research, contributing to a growing body of knowledge that progressively expands our understanding of the universe and its potential for benefiting humankind. The data collected will be shared with researchers worldwide, fostering collaboration and accelerating innovation across numerous scientific disciplines.
Expanding Research Frontiers in Microgravity
The SpaceX ISS Mission Crew-12 will conduct extensive research in materials science, leveraging the unique microgravity environment of the International Space Station. On Earth, gravity significantly impacts material formation and behavior; for example, crystal growth is often distorted and uneven. In microgravity, materials can form with unprecedented purity and uniformity, allowing scientists to study fundamental properties without gravitational interference. This enables advancements in fields like semiconductor development, creating stronger and lighter alloys for aerospace applications, and even producing novel optical fibers with superior performance.
Human health research represents another critical focus during Crew-12’s expedition. Studying how the human body adapts to long-duration spaceflight – including bone density loss, muscle atrophy, and cardiovascular changes – provides invaluable insights into aging and disease processes on Earth. The microgravity environment accelerates these physiological shifts, effectively acting as a ‘fast-forward’ button for observing age-related conditions. This allows researchers to test countermeasures like exercise regimens and pharmaceutical interventions more rapidly than would be possible in terrestrial studies, potentially leading to breakthroughs in preventative medicine.
Biotechnology research also thrives in the microgravity setting aboard the ISS. Protein crystallization is a prime example; larger, higher-quality protein crystals are easier to analyze, revealing crucial structural information that aids in drug design and understanding disease mechanisms. Furthermore, microgravity can influence gene expression and cellular signaling pathways, offering opportunities to explore new avenues for therapeutic interventions and potentially enhance crop production through optimized plant growth processes. The ISS provides a platform to investigate these complex biological phenomena under conditions impossible to replicate on Earth.
SpaceX’s Continued Role in ISS Operations
SpaceX’s ongoing partnership with NASA has become absolutely integral to the continued operation of the International Space Station (ISS), marking a significant shift in how we access and utilize this orbiting laboratory. The upcoming Crew-12 mission, scheduled for launch no earlier than February 15, 2026, exemplifies this crucial relationship. Featuring a crew comprised of astronauts from NASA and ESA (European Space Agency), alongside representatives from other international partners, the mission underscores SpaceX’s role not just as a transportation provider, but as an essential contributor to the ISS’s scientific endeavors and overall sustainability.
A key factor driving NASA’s reliance on SpaceX is the company’s focus on reliability and reusability. The Falcon 9 rocket system, with its ability to be recovered and reused, dramatically reduces the cost per launch compared to traditional methods. This translates directly into more frequent resupply missions carrying vital equipment, research materials, and even replacement parts for the ISS. It also allows for a consistent rotation of crew members, ensuring uninterrupted scientific progress and maintaining a continuous human presence in space – something that would be far less feasible without SpaceX’s innovative approach.
Beyond simply transporting cargo and astronauts, SpaceX is actively shaping the future of low Earth orbit (LEO). The success of Crew-12 and similar missions paves the way for NASA’s ambitions to transition towards a commercially driven space economy. This includes supporting the development of private space stations that could eventually replace or supplement the ISS, fostering greater innovation and expanding access to space for both scientific research and commercial ventures. SpaceX’s reusable technology is therefore not just about cost savings today; it’s an investment in a future where human presence in orbit becomes more commonplace.
The Crew-12 mission represents another milestone in this evolving landscape, demonstrating the effectiveness of public-private partnerships in space exploration. With astronauts Jessica Meir and Jack Hathaway leading the way alongside their international colleagues, SpaceX continues to solidify its position as a vital partner for NASA and a driving force behind humanity’s ongoing presence and research capabilities aboard the International Space Station.
Reliability & Reusability: A Key Advantage
SpaceX’s commitment to reusable rocket technology represents a significant shift in space travel economics, profoundly impacting both the cost and frequency of missions to the International Space Station (ISS). Unlike traditional expendable launch systems where rockets are discarded after a single use, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 booster returns to Earth for landing and refurbishment. This dramatically reduces the per-launch cost – estimates suggest savings of around $60 million compared to older methods – allowing NASA and its international partners to increase the cadence of resupply missions and crew rotations.
The reduced costs enabled by reusability directly translate into more opportunities for scientific research aboard the ISS. With more frequent cargo flights, researchers can send a wider variety of experiments and equipment, accelerating discoveries in fields like medicine, materials science, and fundamental physics. Furthermore, regular crew rotation ensures a consistent presence of astronauts to conduct these investigations and maintain the station’s complex systems. The Crew-12 mission exemplifies this ongoing partnership, contributing to the continuous operation of the ISS.
Looking ahead, SpaceX’s advancements in reusable launch technology are also paving the way for future commercial space stations. NASA’s Commercial LEO Destination (CLD) program aims to transition low Earth orbit activities away from the ISS by 2030 and is supporting private companies like SpaceX and others in developing these new platforms. These commercially operated stations promise expanded opportunities for research, tourism, and in-space manufacturing, building on the foundation established by SpaceX’s reliable and cost-effective access to space.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Human Space Exploration
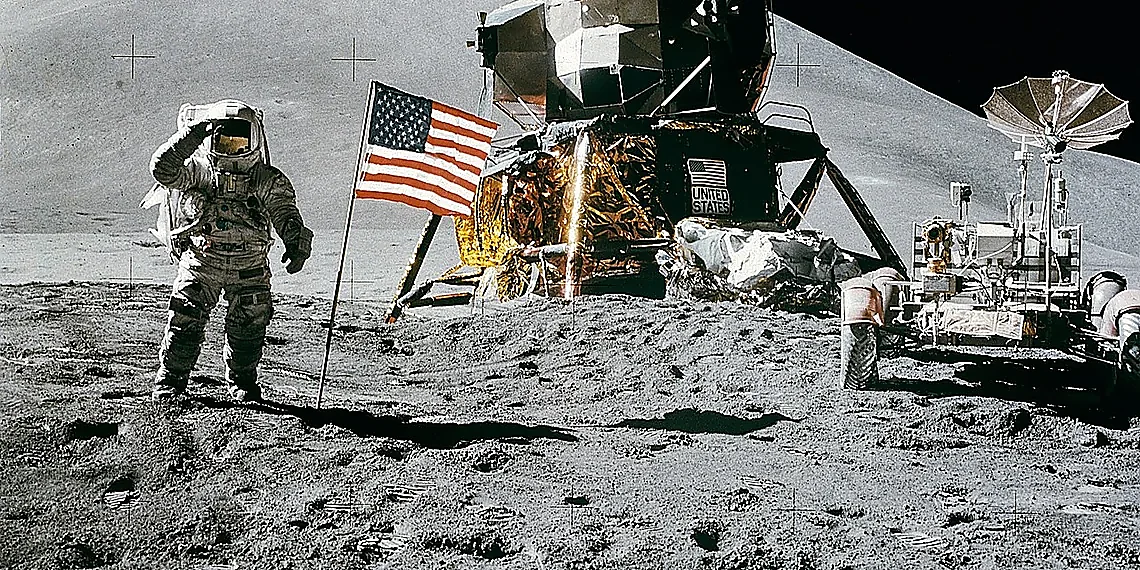
The SpaceX ISS Mission, and missions like Crew-12, represent vital stepping stones towards humanity’s larger ambitions beyond Earth orbit. While the immediate focus is on conducting crucial scientific research aboard the International Space Station – everything from materials science to human health studies in microgravity – these long-duration expeditions are simultaneously building expertise and refining technologies essential for more complex ventures.
The experience gained through missions like Crew-12 directly informs NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon. Understanding how crews operate effectively in extended spaceflight environments, managing resources efficiently, and performing intricate experiments remotely are all lessons learned that will be critical for establishing a sustainable lunar presence. The reliability of SpaceX’s launch capabilities also contributes significantly to the overall success of both ISS operations and Artemis.
Looking further out, the skills and technologies developed through Crew-12 and similar missions pave the way for even more audacious goals – human exploration of Mars. The challenges are immense, requiring advancements in life support systems, radiation shielding, propulsion technology, and autonomous robotics. Each successful mission brings us closer to overcoming these hurdles, proving the feasibility of long-duration interplanetary travel and eventual habitation.
Ultimately, the SpaceX ISS Mission is more than just a scientific expedition; it’s an investment in our future as a spacefaring civilization. The ongoing collaboration between NASA, ESA, and commercial partners like SpaceX demonstrates the power of international cooperation and innovation in pushing the boundaries of human exploration and unlocking the potential for discovery beyond our planet.
The journey of SpaceX Crew-12 has underscored a pivotal moment in space exploration, demonstrating the continued synergy between private innovation and established agencies like NASA.
We’ve seen firsthand how reusable rocket technology, coupled with international partnerships, is dramatically lowering the barriers to accessing low Earth orbit and beyond.
This latest SpaceX ISS Mission exemplifies the power of collaboration; astronauts from the United States, Japan, and France working together on vital research and maintenance aboard the International Space Station represents a truly global effort.
The scientific advancements enabled by this mission, ranging from materials science experiments to investigations into human health in microgravity, will undoubtedly benefit us all here on Earth, while simultaneously paving the way for even more ambitious ventures like lunar bases and Martian settlements. It’s clear that these ongoing endeavors are not just about reaching for the stars; they’re about expanding our knowledge and improving life as we know it. The seamless integration of SpaceX capabilities into ISS operations highlights a new era in space travel, one built on efficiency and shared expertise. To stay abreast of groundbreaking developments like this, and to witness firsthand the continued progress of Crew-12 and future missions, be sure to follow both NASA and SpaceX for regular updates and announcements.
Continue reading on ByteTrending:
Discover more tech insights on ByteTrending ByteTrending.
Discover more from ByteTrending
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.